Breaking addiction is difficult. Those who become trapped look for answers but often meet the unfortunate reality–traditional methods are simply not effective.
This leads many individuals to seek new ways of overcoming addiction. One novel treatment is ibogaine, a psychedelic native to Central Africa, which significantly reduces or even eliminates withdrawal symptoms with one dose.
In this guide, we discuss the benefits of ibogaine treatment for addiction, the addictions ibogaine targets, and the potential dangers of ibogaine treatment.
Understanding Addiction

Addiction to drugs often starts with short-term use, but eventually turns into an everyday habit. With many drugs, this habit creates dependence, where the body is physically unable to function daily without using the specific drug.
This starts in many different ways. Some become addicted from medical prescriptions and others through casual use.
Addiction and dependence create a spiral that makes it nearly impossible for an individual to break their addiction without intervention.
With dependence, the body and brain physically adapt to regular drug use. When the dependent individual stops using, they experience severe withdrawal symptoms like:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Shaking
- Aches
- Depression
- Anxiety
No matter how the pattern starts the result is the same. An individual is left dependent and unable to break free.
Modern Methods

Modern treatments are not very effective. Some treatments put the individual to sleep for long periods. Others force the individual to “tough it out.”
Even worse, medication-assisted therapy transitions individuals onto different addictive drugs. This method merely keeps the cycle of addiction and dependence going.
None of these treatments address physical withdrawal symptoms in the brain. Success rates from traditional methods, like Alcoholics Anonymous programs, are so low because they don’t address the root of the problem.
Ibogaine is different. It has the ability to address withdrawal symptoms in the brain. Thus, ibogaine helps the individual overcome the dependence on a physical level. It is also psychoactive, giving the individual a mystical-like experience that can also be beneficial for overcoming drug addiction.
Ibogaine Treatment for Addiction
Ibogaine is a psychedelic drug extracted from the iboga plant native to Central Africa. For centuries, ibogaine was used for healing and community building in sacred rituals by the native Bwiti religion.
More recently, researchers discovered ibogaine’s positive effects as a treatment for addiction, depression, and PTSD.
Let’s look how ibogaine works in the physical brain to treat addiction, and then examine the mental and spiritual effects of ibogaine treatment.
Physical Healing

Ibogaine’s ability to address physical dependence is its best-known characteristic.
Dependence is often the most challenging part of overcoming addiction. The body cannot function properly without the dependent substance, causing the severe withdrawal symptoms that make quitting drugs difficult.
Ibogaine treats physical dependence by targeting areas of the brain associated with addiction.
There are three ways that ibogaine accomplishes this–healing receptors, neuroplasticity, and as a natural antidepressant.
Healing Receptors
First, ibogaine works as an antagonist, meaning it binds to neurons in the brain associated with drug use and addiction.
Ibogaine utilizes many different receptors–the same receptors that drugs like nicotine, opiates, and alcohol also operate on.
Drug use floods the body with chemicals similar to the body’s natural ones. The drug chemicals attach to natural receptor sites, sending messages to the brain that make us feel good.
However, these chemicals are slightly different, they alter the structure of neurons. Now, the individual’s natural chemical process is ineffective, and they rely on drug use to feel good, or even normal.
When they do try to stop, it takes time for the body to readjust. During this period of adjustment, the body goes through the severe withdrawal symptoms associated with quitting drug use.
Ibogaine acts as a healer. It attaches to neurons and changes them back to their pre-addicted state, while promoting new neurons to grow. This process allows the individual’s natural chemicals to work effectively again.
Thus ibogaine reduces drug withdrawal symptoms–like depression, anxiety, as well as physical symptoms–that commonly begin after stopping drug use.
Neuroplasticity

Next, ibogaine has a mechanism of action that promotes neuroplasticity.
Neuroplasticity is the creation of new pathways in the brain associated with habits.
Habits are an important part of everyday life. As an individual performs a task over and over again, the brain creates pathways to make that task, or set of tasks, easier.
When an individual uses drugs, neural pathways develop that reinforce the activity.
Ibogaine’s neuroplasticity effect helps reset areas of the brain responsible for these habits. It stimulates cell growth and helps the brain create new habit pathways and replace old ones.
The individual is able to change their addictive patterns to healthy ones almost overnight. And because noribogaine, the byproduct of taking ibogaine, stays in the body for a much longer period of time, the individual gets the benefits of this neuroplasticity weeks after taking ibogaine.
This makes overcoming addiction, and breaking the habits formed during addiction, much more manageable.
Antidepressant

Lastly, ibogaine works as a reuptake inhibitor for serotonin.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that sends signals by connecting to neurons in the nervous system. These signals give the individual feelings of joy, accomplishment, and help promote stability.
Typically, serotonin is produced, used, and then reabsorbed back into the body. However, ibogaine blocks this reabsorption action and keeps serotonin available for neurons to use and reuse.
Antidepressant drugs work in the same way–making ibogaine a natural antidepressant.
With more serotonin available, ibogaine counteracts the negative effects of drug withdrawal. Effects last for weeks, through noribogaine, and are beneficial in promoting long-term change after ibogaine treatment.
Briefly, let’s look at noribogaine and how it works.
Noribogaine

After taking ibogaine, the body metabolizes it into noribogaine.
Noribogaine is similar to ibogaine but without psychedelic properties. It continues to work on the individual by providing healing and offering antidepressant effects long after taking ibogaine.
That’s because noribogaine has a much longer half-life than ibogaine.
A half-life is the amount of time it takes the body to metabolize, or eliminate, a drug.
Ibogaine has a half-life of 4-7. It typically takes 35 hours for the body to deplete the majority of the ibogaine taken.
However, noribogaine’s half life is much longer, 28-49 hours. Noribogaine remains in the body for ten or more days after taking ibogaine.
During this time, noribogaine continues to provide the benefits of ibogaine. It offers a mood boost, helps control cravings and withdrawals, and heals areas of the brain damaged by addiction.
Changing without intervention is difficult; ibogaine helps address the physical drug dependence, leaving the individual in a strong position to make better decisions and form new habits moving forward.
But this immediate physical healing isn’t the end as ibogaine continues to stay active in the body for an extended period of time.
Mental and Spiritual Improvement

Ibogaine’s unique effect on the physical level is compounded by the psychedelic experience. Ibogaine’s psychoactive properties offer the individual insight important for creating lasting change.
Let’s look at the different phases of the psychedelic experience with ibogaine and then discuss these benefits.
Three Phases of Ibogaine

The ibogaine experience has three distinct phases. Each phase is important for the spiritual and mental health benefits of ibogaine.
Phase I – Waking-Dream
4-8 Hours
The first phase is the most intense. Those who take ibogaine describe it as a “waking-dream”–like being almost asleep. They see visions of past decisions or traumatic experiences, but in a new light. With this fresh perspective, the individual finds peace and acceptance.
Phase II – Introspection
8-20 Hours
The next phase of ibogaine is a deeply reflective one. With the visual properties of the ibogaine worn off, the individual feels a powerful sense of awe.
The individual is awake and alert and spends time thinking.
The lessons and experiences from the first phase of ibogaine are still alive in the user’s mind. They continue to learn, accept, and understand more about their life, past decisions, and how to create a better future.
Phase III – Afterglow
Up to 72 hours
The afterglow phase is the final phase of ibogaine. Typically, this phase lasts up to 72 hours after taking the flood-dose.
During this phase, the individual reflects on the other two phases of ibogaine. Journaling is encouraged during this time. Writing about their experience, their feelings, and what they learned, helps reinforce the experience.
Now that the intense effects of ibogaine have worn off, the patients typically prefer to be active. They enjoy wandering around their environment in deep thought or participating in discussions with others.
Once the ibogaine completely wears off, the user often sleeps for 4-12 hours, which concludes the psychedelic experience of ibogaine.
Mental Benefits of Ibogaine

Modern medicine is looking for ways to utilize the benefits of ibogaine while removing the psychedelic experience. But this may impact the effectiveness.
The ibogaine experience is intense. However, studies have shown that this experience offers benefits beyond the physical healing properties, such as:
- Reduced anxiety
- Reduced depression symptoms
- Increased psychological wellbeing
- Positive impact on mental health
These mental benefits come from the psychedelic experience itself. Getting off drugs is often nearly impossible because of the effects of depression. The psychedelic experience offers insight that eliminates the feelings of depression contributing to the addiction spiral.
This is not just a benefit of the physical treatment in the brain. The psychedelic experience itself gives the individual these benefits.
One study suggested those with the “highest insightful and mystical experiences showed the most benefit.”
Without this psychedelic experience, the lasting effects of ibogaine may be severely limited.
Spiritual Benefits of Ibogaine

Spirituality is the feeling that something greater than you exists–that your life has meaning and purpose.
A high-dose psychedelic experience often leads to a so-called “ego-death.” This is a mystical feeling where the individual self becomes encompassed by the world. Ego-death includes a sense of oneness with the planet and all peoples.
Although the mental effects are measurable, accounting for spiritual benefits is more difficult.
Anecdotal evidence shows many who leave an ibogaine experience feel that their life has new meaning and purpose. These types of emotions create a dramatic change. That kind of event is often necessary to break free from years of drug abuse and negative compounding habits.
The spiritual experience, along with the physical and mental benefits, make ibogaine so special. Ibogaine is unique in its mechanism of action for drug addiction, which makes it a powerful treatment for minimizing withdrawal symptoms and inspiring a powerful life change.
Now that we understand how ibogaine works and the benefits of ibogaine treatment for addiction, let’s look at the addictions that ibogaine treats and how ibogaine specifically works for each addiction.
Specific Addictions

Ibogaine helps with many drug addictions. The effectiveness of ibogaine may vary from substance to substance. However, each drug in this list has shown positive potential through scientific research.
Heroin and Opiates
Heroin and opiate addictions are among the most dangerous and deadly worldwide. These substances have a high potential for abuse, and more harmful versions are on the rise.
Because these drugs cause dependence, breaking free of opiates is extremely difficult. The withdrawal symptoms are intense, and can be deadly.
Opiates originally come from the opium poppy plant–a natural source of opium. Usually the opium plant synthesizes down to a more pure form called morphine–which was historically the base for drugs like heroin and most prescription drugs.
Opiate Treatment Process

Ibogaine is almost tailor-made by nature to treat opiate and heroin addiction. Taking ibogaine is safe after a few hours of the last dose of short-acting opiates.
During treatment, ibogaine binds to the opioid receptors in the brain responsible for opiate effects and addiction.
It acts similar to methadone in that it blocks these receptors. However, unlike methadone and other traditional treatments, ibogaine’s healing properties work to reset and repair the brain areas responsible for opiate addiction.
Through this multi-functional healing approach, ibogaine eliminates the majority of opiate or heroin withdrawals.
These effects are immediate and lasting. The noribogaine in the system, and the spiritual and mental benefits, go a long way in helping the individual recover.
Studies on Ibogaine for Opiate and Heroin Addiction

Here are some of the reported research outcomes from studies on ibogaine treatment for addiction to opiates and heroin.
“Blockade of opioid withdrawal symptoms and no further desire to take heroin in the days following treatment.”
“Patients reported diminished opioid craving and significantly improved mood after treatment. Interestingly, these effects persisted over a long period based on self-reports at a 1-month follow-up interview.”
And another study describes the longer-term effects:
“A single ibogaine treatment reduced opioid withdrawal symptoms and achieved opioid cessation or sustained reduced use in dependent individuals as measured over 12 months.”
These clinical outcomes, along with hundreds of anecdotal stories of individuals attending ibogaine clinics around the world, show the power of ibogaine for treating addiction to heroin and opiates.
But the world has changed in the last decade. Many heroin and opiates found today no longer originate from the opium poppy, they are chemical creations called fentanyl.
Rise of Fentanyl

Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is 100 times stronger than morphine. Because of its synthetic nature, production is cheap and easy.
Due to fentanyl’s differences from other naturally produced opioids, an individual using fentanyl, or fentanyl-laced drugs, must undergo an extended waiting period before ibogaine treatment.
Taking ibogaine with fentanyl in the system is dangerous or even deadly. Typically, fentanyl clears the system in 5-7 days. Only then is ibogaine safe.
During this period, treatment involves a switch to morphine-based or other natural short-acting opiates to relieve withdrawal symptoms. After completing detoxification from fentanyl, they are cleared for ibogaine treatment.
Most drugs purchased on the street today–opiates, heroin, and even other drugs–contain fentanyl. Drugs not purchased from a pharmacy most likely contain fentanyl. For this reason, most patients taking ibogaine today must detox from fentanyl before treatment begins.
Suboxone and Methadone

The last form of opiates is the long-acting, or “sticky,” medications. These drugs include Suboxone (buprenorphine and naloxone) and methadone, both are frequently-abused prescription drugs .
Doctors give long-acting opiates to those suffering from opiate addiction. Unfortunately, in many cases, these drugs become the addiction.
Suboxone and methadone work differently from short-acting opiates. They are sticky, meaning they bind to receptors blocking the effects of opiate use. They act as a deterrent, hopefully keeping individuals from further drug use.
Because of their primary function these drugs have a longer half-life, which means the drug remains in the system for much longer than short-acting opiates.
For ibogaine treatment, this is a problem. Not only do Suboxone and methadone block ibogaine’s effectiveness, but they can also lead to complications or even death when mixed with high levels of ibogaine.
Methadone or Suboxone users typically must wait 15-45 days before taking ibogaine. In some instances, a low-dose protocol treatment begins earlier, but first most of the detoxification process must be complete.
Ensuring an individual is clean from these long-acting opiates with accurate blood testing is vital before taking ibogaine.
Alcohol

Alcoholism is one of the most prevalent diseases in the USA. Over 10% of Americans have alcohol use disorder, making it difficult for them to control their drinking habits.
Ibogaine is an effective treatment for alcoholism. Although the exact mechanism of action is unclear, studies show that ibogaine may positively affect regulation and areas of the brain associated with alcoholism.
But alcohol is different from other drugs. The withdrawal from alcohol is painful and can be deadly–even more deadly than heroin.
That is why getting off of alcohol typically requires medical intervention.
Alcohol, Ibogaine, and the Liver

When using alcohol for long periods, it begins to have effects on the liver and liver enzymes.
For those considering ibogaine, these liver enzymes are necessary for the body to break down the ibogaine and safely metabolize it out of the system.
If liver enzymes are not stabilized, ibogaine and alcohol can be a deadly mix.
The detox process is necessary for the safety of these individuals. Before administering ibogaine, clinics make sure liver enzymes are at safe levels, either naturally or through medications.
Typically, detoxing from alcohol and stabilizing these liver enzymes takes around 5-10 days.
During this time, nurses must monitor these patients. The individual stays under medical supervision to ensure positive vital signs and withdrawal symptoms do not pose an immediate danger.
Once the liver enzymes have stabilized, ibogaine treatment begins.
Methamphetamine

Methamphetamine is a powerful stimulant drug. At high doses, methamphetamine can be very dangerous. Over time, using meth has severe adverse effects.
Like any drug, methamphetamine use changes the way the brain functions. This makes it challenging to overcome methamphetamine addiction.
Short-term methamphetamine withdrawals are not as severe as heroin or alcohol. However, the long-term, habit-forming, and addictive nature of methamphetamine makes it hard to overcome.
Ibogaine treats methamphetamine by providing physical healing and rewiring that changes these habit patterns. In this way, ibogaine works differently from traditional treatment methods relying only on time.
The psychedelic properties of ibogaine are also helpful for escaping methamphetamine addiction. Through these mystical experiences, individuals find purpose and meaning, as well as a desire to change.
Studies show that ibogaine helps regulate habitually formed behaviors for those with methamphetamine addiction.
Methamphetamine must detox entirely from the system before taking ibogaine. Typically, it takes 3-5 days of detox before taking ibogaine for methamphetamine addiction.
Cocaine and Crack

Cocaine and crack–or freebase cocaine–are dangerous, addictive drugs.
These addictions are a severe problem in the USA, and cocaine deaths are on the rise.
Because of their addictive nature, breaking free from cocaine or crack addiction alone is challenging.
Ibogaine works in the physical brain to heal and renew areas associated with crack and cocaine addiction.
And through the psychedelic experience, ibogaine helps individuals find solid and personal reasons to change their lifestyle and improve themselves.
Here are the findings from one study on ibogaine for cocaine addiction:
“The results demonstrated beneficial after effects of ibogaine detoxification on drug cravings in cocaine-dependent subjects reported at 1-month assessments.”
Before taking ibogaine, cocaine must be completely out of the system. It typically takes 3-7 days for cocaine or crack to be detoxed.
Once the individual’s system is clean, they are cleared to take ibogaine.
Nicotine and Tobacco

23.6 million people in the USA suffer from addiction to nicotine–the main drug found in tobacco products. Although the addiction to this drug doesn’t have a high potential for overdose, the long-term negative cognitive, neurological, and physical health effects can be devastating.
With that, nicotine and tobacco are among the most addictive drugs available. Which is what makes quitting so difficult.
Ibogaine shows promise for treating nicotine addiction. Ibogaine targets the nicotine receptors in the brain. In this way, ibogaine helps reduce withdrawal symptoms from nicotine and address addictive behaviors.
In one preclinical study, the results of ibogaine for nicotine addiction were positive.
“These results suggest that noribogaine dose-dependently attenuates drug-taking behavior for nicotine and attenuates the reinforcing effects of nicotine.
‘The findings from the present study hold promise for a new therapy to aid smoking cessation.”
Nicotine should not be mixed with ibogaine. The individual typically must wait around 24 hours before taking ibogaine after using nicotine. This is just a safety precaution.
Other Addictions

From a dependence point of view, the drugs previously mentioned are the most physically addictive. However, that does not mean breaking other drug or habit-based addictions isn’t difficult.
Research into these other addictions is limited, especially in relation to ibogaine.
However, ibogaine’s ability to reduce depression, reset and rewire the brain, and offer mental healing through the psychedelic experience offer a potential treatment alternative for many addictions.
These include:
- Marijuana
- Kratom
- Video Games
- Food Addiction
- Pornography
- Social Media
And countless other habit-based addictions.
Ibogaine is helpful in breaking these addictions and finding new purpose and meaning.
Dangers of Ibogaine
Although ibogaine has its benefits, there are also potential dangers for anyone considering ibogaine treatment for addiction.
Ibogaine seriously threatens those with certain health conditions or when taken without medical supervision.
Let’s review the potential dangers of ibogaine.
Cardiovascular Dangers
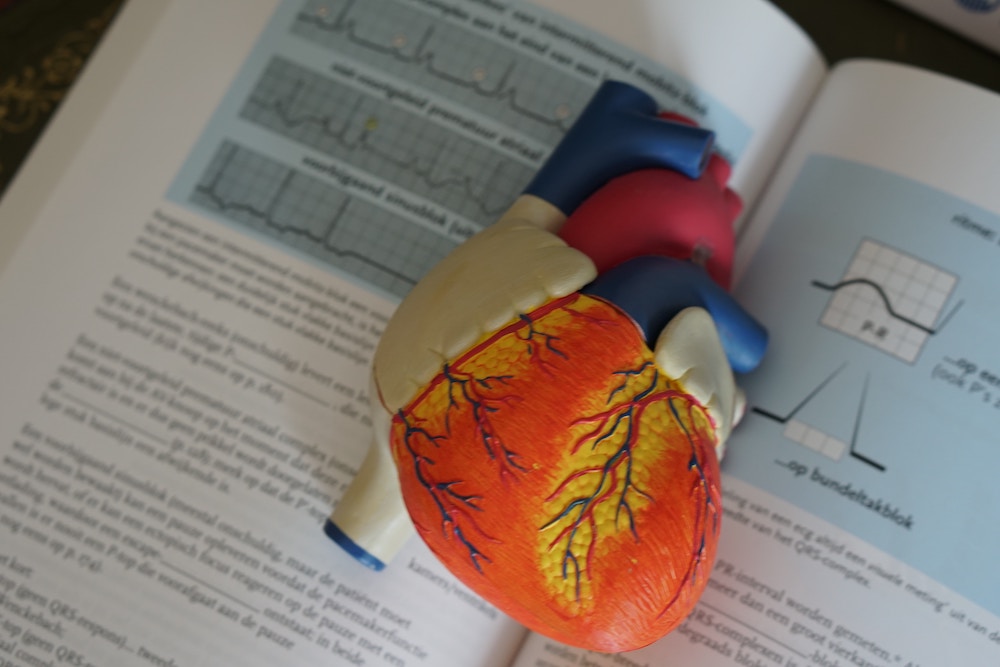
The first, most well-established danger is ibogaine’s effects on the heart.
Ibogaine may prolong the QT interval in individuals who take it. This effect lasts for up to 42 hours after taking ibogaine.
High doses potentially cause irregular heart arrhythmia, which is dangerous.
Those with pre-existing heart conditions should not seek ibogaine treatment, due to its potential dangers.
Additionally, taking ibogaine without proper prescreening in a medical setting is not advised. Individuals may not be aware of heart abnormalities.
Through prescreening, medical experts determine if your heart is healthy enough for ibogaine.
Proper prescreening and monitoring reduce the dangers of ibogaine and heart irregularity.
Ibogaine and Drug Interactions

Secondarily, ibogaine poses a danger when certain drugs are still in the system. These drugs lead to potentially severe complications and even death.
Some illicit drugs, as previously described, metabolize and clear from the body within a specific time. These drugs include:
- Alcohol
- Fentanyl
- Suboxone and Methadone
- Methamphetamine
- Cocaine and Crack
Ibogaine should not be taken while these drugs are present. Simple bloodwork and testing can ensure the elimination of these drugs before taking ibogaine.
Other drugs to avoid taking with ibogaine include:
- SSRIs and Antidepressants
- Antihistamines
- Antifungals
- HIV Medication
With proper prescreening and planning, the dangers presented by these drugs and ibogaine are avoidable.
Prescreening and Medical Monitoring

The best way to reduce negative outcomes from ibogaine treatment is prescreening and medical monitoring.
Proper precautions and medical staff make ibogaine treatment safer. Here is the process ibogaine clinics take today to create safer experiences for those taking ibogaine.
Prescreening
Before attending a medical ibogaine clinic, patients answer certain questions determining their health, heart, and medical status.
Patients that travel to a clinic but cannot undergo treatment for medical reasons end up paying unnecessary costs. Proper screening helps reduce treatment costs for these individuals.
Medical Examination
Once patients arrive at the clinic, they receive rigorous medical testing–including EKGs and bloodwork–ensuring they are healthy for treatment.
The medical examination also determines the levels of different drugs and substances in the system. With this information, the doctor establishes whether the patient needs detoxification time.
Testing continues until the patient clears detoxification protocols.
Treatment Monitoring
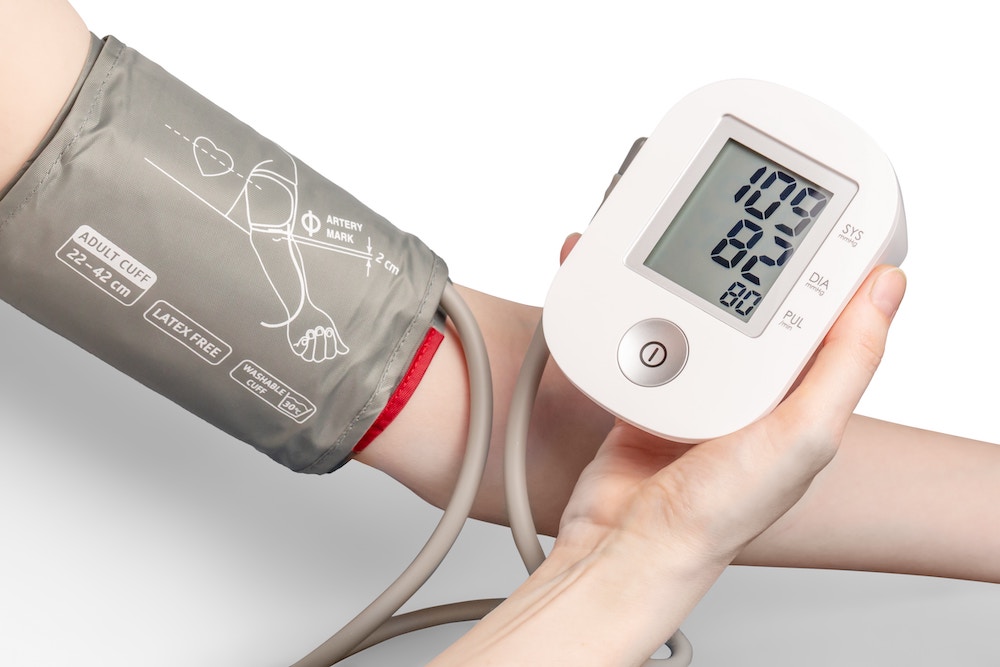
Lastly, monitoring patients with a professional, experienced medical team and modern medical equipment reduces unfavorable outcomes from ibogaine treatment.
Constantly monitoring vital signs, especially heart rate and blood pressure, increases the likelihood of successful treatments without negative outcomes.
With the right medical team, proper prescreening, and testing, adverse outcomes from ibogaine are drastically reduced.
This does not eliminate the risk but significantly reduces it.
Is Ibogaine Right for Your Addiction Treatment?
Ibogaine is not a cure. But for those who previously tried traditional methods without success, ibogaine provides an alternative.
Addiction is difficult to overcome. However, ibogaine is a promising treatment method with proven success in helping overcome withdrawal symptoms for those struggling with addiction.
Everyone deserves a life free from addiction.


